Nearly two-thirds of U.S. households use electric heaters as a supplemental heat source. Combinations with a gas furnace are particularly popular. According to the RECS, only 26% of homeowners consider electricity as their only heating method. And most of them live in the Southwest, where heating a home with low-power electric units is economically feasible. BHC&Air offers comprehensive solutions for energy-efficient electric heating of homes and commercial facilities: keep everyone warm!
What is Electric Heating System?
Electric heating systems are extremely diverse, but the principle of operation is the same – the energy system transforms electrical energy into heat and redistributes the energy between rooms by radiating devices. In centralized systems, the heating devices are radiators, electric heat pumps and floor heating systems. For local heating, they use electric heaters.
Heating with Electricity: How Does That Work?
Heating houses with electricity was made possible by the thermal action of electric current (Joule-Lenz law) – the heating of a conductor as a result of the conversion of the kinetic energy of electrons. The electric current overcomes the resistance of the conductor and operates, as a result heat is released and the air is being heated, so heating systems based on the thermal action of the current are also called resistive. In order to increase heat production, resistive electric heaters are made of heat-resistant conductor alloys with high resistivity – nichrome, chromal, ferronichrome and fechral.
Resistive electric heaters demonstrate maximum efficiency. Almost all the power consumed by the system is spent on heat production, but most of the heat is lost during transmission. So electric heating is more expensive than gas heating, but at the same time cheaper than liquid fuel heating. For example, according to the EIA, Americans paid an average of USD 1,072 per season for electric heating in the U.S. in the winter of 2023-24, while heating with liquid fuels cost USD 1,722, respectively, and electricity rates are expected to increase by 3% per year or more in the coming years.
Types of Electric Home Heating
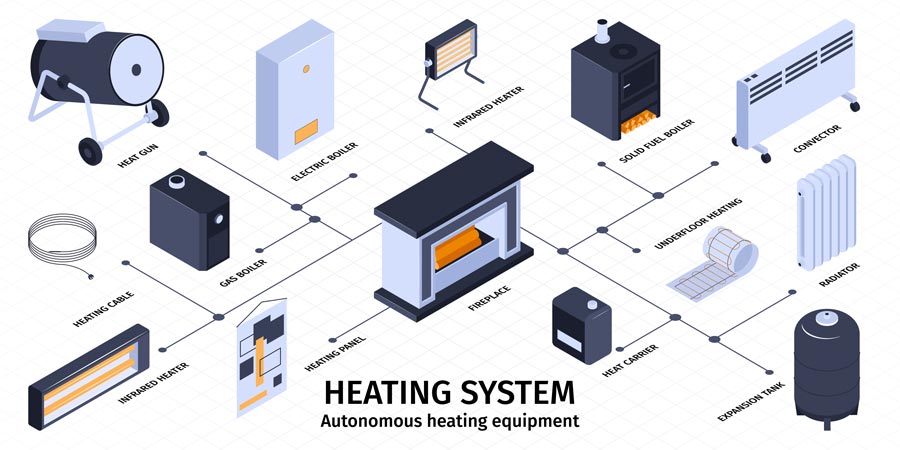
Electric space heating can be performed by direct (no coolant) or indirect (using coolant) heat transfer from heated conductive elements. Direct electric heaters include electric furnaces, convectors, infrared heaters, heat fans, under-floor convective heaters and cable and film heating systems designed for installation under the floor. The principle of indirect heating is embodied in central heating systems: the heat source is an electric boiler or tank heater, and the heat carrier is water.
Alternative classification – by radius of action: local heaters heat one room, central heating systems serve several rooms at the same time. For stationary local heating, wall and floor convectors are usually used. They are inexpensive, low-power devices with a tubular electric heater as the heating element.
One convector serves one room up to 30 square meters. For aesthetic reasons, it can be built into the building envelope. Mobile heaters can be conveniently moved from room to room as required, but the unit should not be left unattended – an open coil increases the risk of smoke and fire. IR heaters are equipped with a quartz emitter that converts electricity into IR rays that heat individual surfaces directly in front of the heater, thus significantly reducing energy costs.
Dynamic storage type heaters have a prolonged action, radiating heat even after power failure, so they are convenient to use in multi-tariff systems with unstable power supply. Around the heating element there is a buffer made of fireclay and natural stone, which absorbs heat energy and releases heat; the intensity of heat transfer is regulated by a fan.
Film floor heating systems with built-in conductors are installed under linoleum and laminate flooring, while cable systems are installed under screed. Baseboard tube heaters are also on the market, with conductive elements inside tubes placed around the perimeter of the room on the window side three-quarters of an inch above the floor; the ribbed surfaces of the tubes enhance heat output. The advantages of floor and baseboard heating include even heat distribution throughout the room, concealed installation, and fast heating without drying out the air.
Central heating systems are divided into two types – duct and hydronic. In duct systems integrated with ventilation, the heat generator is an electric furnace with a fan for blowing warm air into the air duct. In hydronic systems, heat is generated by an electric boiler connected to the radiators through a closed circuit in which water is circulated by a circulation pump. Moreover, it is possible to connect water underfloor heating to the radiators.
Electric heat pumps are a more modern alternative to resistive heating systems, using electricity to supply warm air from the outside environment. A heat pump is recognized as one of the most economical ways to heat: the energy cost of heat transfer is four times lower than powering a compressor unit. According to the EIA, the use of heat pumps reduces the energy intensity of heating systems almost twofold.
In winter, the heat pump combines heating and air conditioning functions, and when the weather gets warmer, it switches to air conditioning mode. In regions with mild winters, the heat pump can serve as the only source of heat. And in colder climates it is used as a supplement to the main heating.
Heating with Electricity: Options and Tips
Building a heating system requires a large upfront investment, but electric heating installation can be made cheaper by having a qualified HVAC contractor design the project. BHC&Air’s engineering department can help you calculate and select energy-efficient equipment to fit your budget, and you can take some steps to reduce your energy needs yourself:
- switch to multi-tariff metering of energy consumption – this will reduce operating costs by up to 40%;
- choose energy efficient equipment with a short payback period;
- seal walls, floors and ceilings properly;
- place convectors under windows to prevent heat leakage;
- use IR heaters in non-residential areas and outbuildings;
- install thermostats and controllers for weather-dependent regulation.
Benefits of Electric Heating System
Electric heating is not the cheapest, but it is an exceptionally comfortable and environmentally friendly method of heating, eliminating dirt and soot in the house, suffocating smell of burning and toxic emissions. The costs of installation and procurement of equipment, except for heat pumps, are quite moderate. There is no need for complex and labor-intensive work, but there are interesting offers.
Electric heaters are characterized by their compact dimensions and unobtrusive minimalist design, which harmoniously fits into every interior and lifestyle. Practically speaking, electric heating offers many advantages that partly offset the operating costs:
- easy installation and maintenance;
- wide range of models;
- programmable temperature settings;
- low inertia and auto-regulation;
- high level of reliability and safety;
- possibility of zone heating;
- low noise level;
- no installation permit required;
- combinability with other heating systems.
Costs of Switching to Electric Heat
For the sake of the environment, many homeowners are considering switching from fossil fuels to electric heating, but this is not easy. To power electrical equipment, it is often necessary to change the wiring and reconstruct the power grid; the total investment in wiring is USD 3000-5000.
Add to this the cost of purchasing equipment and labor for the installation team and you get a five-digit figure. According to the EIA estimates, converting a hydronic system to an electric boiler will cost USD 5000-7000, and the cost of preparing the infrastructure for the installation of an electric heat pump sometimes reaches up to USD 42000, and that’s not counting the cost of the equipment itself!
How Much Does Electric Heater and Installation Cost?
The cost of electric heating depends on the type of equipment: electric boilers are the cheapest and cost USD 800-7000 plus USD 700-2000 for installation and connection. Electric furnaces are quoted higher – USD 2047 to USD 7743 per unit and USD 1500-5000 for installation. And heat pumps are even more expensive – USD 4000-5000 for a standard model and USD 7000-9000 for modifications for cold climates. Taking into account that a medium-sized house needs two pumps, and a large country residence needs at least three, the purchase of equipment will cost USD 18000-26000.
The easiest way to calculate the approximate cost of installing electric heating is to use an online calculator, and a BHC&Air manager will announce the exact amount after his/her professional calculation. Even if the upcoming costs are frightening, do not rush to abandon the project: we help you optimize the estimate and close the budget deficit.
Average DIY Cost vs. Hiring a Pro
Unlike gas equipment, in most cases the independent installation, replacement and maintenance of electric heating systems is not punishable by law. If you are confident in your abilities, have sufficient skills and have managed to acquire professional installation tools, you can save up to USD 5000 on contractor’s services depending on the scope of work.
The cost of installing electric heating is calculated based on the hourly rate, which varies from USD 50-200 per hour; at the same time, the installation of heating equipment takes an average of two to three hours. As you can see, professional installation of the heating system is not so expensive. If you have no experience in installation work, it is better not to risk and trust the experts, because to correct mistakes and deal with the consequences is more expensive!
The Best Electric Heating for Homes
Which heating system to declare the best is a question that has no single right answer. The choice depends on your goals and priorities. If saving money is important, look for film systems and storage heaters. If you need zone heating, go for a hydronic system led by an electric boiler. In the Central States and Midwest, the combination of a gas furnace and heat pump is a popular choice, and many homeowners are convinced that it offers the best balance of thermal comfort and operating costs.
One way or another, each project requires an individual approach. Therefore, we suggest resolving all doubts in consultation with a BHC&Air expert and leaving an application for electric heating calculation on our website. A duty manager will contact you shortly to clarify the details, while you make a list of tricky questions we are glad to answer!